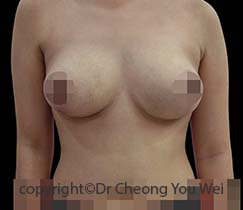
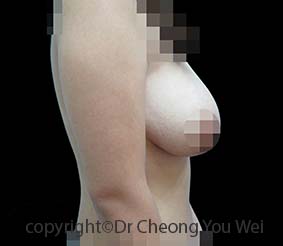
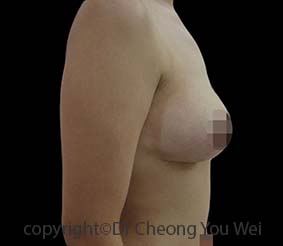
Breast Reduction
- Before
- After
- Before
- After
Excessively large breasts (macromastia) can cause both physical and emotional distress for patients. Patients with macromastia may experience physical discomfort resulting from the weight of their breasts. Shoulder pain, neck pain, chronic headaches, back problems, and skin rashes beneath the breasts, painful bra strap grooving in the skin are common problems encountered. The resulting burden can make it challenging for patients to perform common physical activities. The undue prominence of large breasts may attract unwanted attention and comments from others. Patients may suffer from emotional distress or mental health problems as a result of their large breasts. Large breasts may make it difficult for patients to wear fashionable clothes that they desire. Large breasts also tend to be saggy and affect the aesthetic impression of the breasts.
Breast reduction is a surgical procedure that reduces the size of the breasts by removing excess glandular tissue, skin and fat. The nipples are also lifted from their saggy positions and the breasts are reshaped to become smaller and uplifted. The indications for breast reduction surgery are three-fold – physical, psychological and aesthetic. Breast reduction restores physical comfort, freedom, and self-esteem from the physical and mental burdens of excessively large breasts. Although breast reductions are commonly performed for functional reasons, there is a cosmetic benefit as well, as the breasts are also lifted into a more youthful position in breast-reduction operation. In conventional breast reduction surgery, a tissue pedicle is created from the existing breast tissues to construct a new and smaller breast mound. The pedicle also lifts the nipple-areola complex from its original saggy position to a new and higher site. Excess breast tissue and skin are removed. The remaining skin is re-draped onto the new breast mound to create a smaller and uplifted breast.
The use of liposuction for breast reduction is possible but limited. Breasts are consisted of both fatty tissue which can be removed by liposuction, and glandular tissue which can only be removed by surgical excision. Additionally, liposuction cannot remove excess skin of the breasts, so the breast will remain saggy even though the volume is partially reduced by removal of fatty tissue.
Preparation
-
Inform the doctor of any pre-existing medical conditions and drug allergy. All medical conditions must be treated and stabilized before surgery.
-
Stop smoking at least one week before surgery. Smoking is harmful to wound healing and increases the risks of other post-operation complications.
-
Stop the following medications and supplements from one week before surgery until one week after surgery.
-
All supplements containing vitamin E, ginseng, ginkgo, garlic, fish oil, and other ingredients that increase bleeding during the procedure. Other supplements, traditional medicine, and herbs, in which ingredients are unknown, have to stop as well.
-
Medicine that increases bleeding during the procedure such as aspirin, NSAIDs, and warfarin. However, you may need to consult your physician who prescribed the medication before you stop them.
-
-
On the day of surgery, wear simple and comfortable clothing. Do not wear any makeup. Do not wear any jewelry and metal objects on the face and body.
Surgery
Duration: 3-4 hours
Anaesthesia: General Anaesthesia
Hospitalization: One day
Recovery*: Back to work in 7 days, light exercise after one week, heavy exercise after 4 weeks. * The actual speed of recovery may vary from person to person.
Surgery Technique:
Three options are available:
-
Vertical short scar technique: an incision is made around the areola, with another vertical incision from the areola down to the breast’s lower edge, forming a “lollipop-shaped” scar. Compared to the inverted-T technique, vertical short scar technique produces a much shorter scar and the overall shape of the breast looks more natural and uplifted. Vertical short scar technique is the technique of choice in our practice.
-
Inverted T technique: an incision is made around the areola, with another vertical incision from the areola down to the breast’s lower edge, plus a horizontal incision along the lower border of the breast. Among all the techniques in breast reduction, this technique produces the most scars on the breast. Inverted-T technique is used for very large breasts.
-
Periareolar reduction: The only scar is around the areola. This technique only works when just a small amount of tissue needs to be removed.
Post-operative Care**
-
What to expect:Swelling usually peaks on the second to third day after surgery and will gradually subside after that.
-
General care:
-
Wear a special supportive bra for at least one month.
-
Avoid smoking for at least one month. Smoking increases the risk of wound complications.
-
Sleep on the back. Avoid sleeping on one side to prevent pressure on the breast.
-
Adequate rest and sleep are helpful for a speedy recovery.
-
Be relaxed and calm. Contact the clinic if there are any queries.
-
-
Medicine: Finish the oral antibiotics as prescribed. Take the painkiller when necessary.
-
Wound care:Leave the wound dressing on until coming back for review. Change the dressing if it gets dirty or soaked. After removing the wound dressing later, clean the wound with a clean cotton tip soaked with sterile water/saline. Apply antibiotic ointment.
-
Physical activity:Avoid heavy physical activity and exercise for at least one month.
-
Follow-up: Come back one week after surgery for review.
-
Emergency: If there is heavy bleeding, a rapid increase in swelling or severe pain, contact the clinic/doctor for advice immediately.
** The instructions in this list are only for general guidance. If you have any specific queries or concerns during the post-operative recovery, please contact the clinic for further advice.