Fat Graft
Fat grafting, also known as fat transfer, is a procedure in which fat is transferred from one area (donor area) of the body to another area (target area or recipient site). Fat graft is used to fill up and enhance target areas where tissue volume is diminished or lost due to aging, trauma, or congenital anomaly. Fat graft has been used to improve and enhance cosmetic appearance of the face, breast, hands, buttocks and other parts of the body.
Fat graft is composed of 2 main components: fat cells and stromal vascular fraction (SVF). SVF contains heterogeneous cell populations such as adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and variety of immune cells. SVF has regenerative property that enhances fat graft survival and stimulates regenerative changes in cells and tissues at the target sites and the surrounding areas. Besides filling up and improving and the cosmetic appearance of the target areas, fat graft also has therapeutic effects in the repairs of wounds, scars and damaged tissues. Fat grafting enjoys the benefits of abundant supply, ease of harvesting, and generally low rate of complications.
Fat graft procedure involves three steps:
-
-
-
Harvesting of fat graft from donor area using liposuction technique (see Liposuction)
-
Separation and purification of fat graft
-
Injection of fat graft into the target area
-
-
After injected into the target site, fat graft will undergo revascularization and incorporates into the target area. Certain percentage of the fat graft may fail to blend in and undergo resorption and disappear. Revascularization and incorporation will take about six months to complete. Fat graft that successfully blend in will remain in the body for long term.
The use of correct techniques of harvesting, purification, and injection significantly improve the survival and success rate of fat grafting. The use of specialised fat grafting instruments such as MAFT Gun© allows for atraumatic harvest of fat graft and precise injection of ultra tiny fat droplets to the target sites. This helps to ensure accurate placement of fat graft and preserve the health and survival of the fat graft to achieve desirable and long-lasting results.
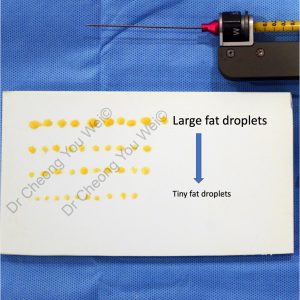
Fat Droplets in fat grafting.In fat grafting, fat is injected into the recipient site in the form of multiple fat droplets. A good fat graft injector can deliver very tiny fat droplets that can ensure precise placement, better survival rate and reduced complications of fat grafts.
Common applications of fat grafting:
-
-
-
Face: to restore youthful appearance by adding volume to hollow or wrinkled areas such as the cheek, temples, nasolabial folds. Fat graft can also be used to enhance areas such as the lips and forehead to make them look fuller and more supple. (see Fat Graft to Face)
-
Periorbital areas: Fat graft can correct hollow upper eyelid and tear trough below the eyebag.
-
Breast: fat graft can be used for breast augmentation (see Breast Augmentation by Fat Graft), correct breast asymmetry, repair damaged breast tissues, and correct scar deformity from previous breast surgery.
-
Buttocks: fat graft is used in Brazilian buttocks lift (see Buttock Lift)
-
Scars: Fat graft can reduce the appearance of scars on the face and body, resulting in softer and healthier skin.
-
Hands: to fill and rejuvenate the dorsum of the hand by covering the visible veins and tendons with fat graft.
-
-
Preparation
-
Inform the doctor of any pre-existing medical conditions and drug allergy. All medical conditions must be treated and stabilized before surgery.
-
Stop smoking at least one week before surgery. Smoking is harmful to wound healing and increases the risks of other post-operation complications.
-
Stop the following medications and supplements from one week before surgery until one week after surgery.
-
All supplements containing vitamin E, ginseng, ginkgo, garlic, fish oil, and other ingredients that increase bleeding during the procedure. Other supplements, traditional medicine, and herbs, in which ingredients are unknown, have to stop as well.
-
Medicine that increases bleeding during the procedure such as aspirin, NSAIDs, and warfarin. However, you may need to consult your physician who prescribed the medication before you stop them.
-
-
On the day of surgery, wear simple and comfortable clothing. Do not wear any makeup. Do not wear any jewelry and metal objects on the face and body.
Procedure
Duration: 1 to 3 hours
Anaesthesia: Local anaesthesia for most cases. Large areas such as buttocks may require general anaesthesia.
Hospitalization: not required except the cases that require general anaesthesia
Recovery*: Back to work in 3-5 days, light exercise after one week, heavy exercise after 4 weeks. * The actual speed of recovery depends on the size and extent of the fat grafting and may vary from person to person.
Technique: the procedure consists of 3 steps:
-
Harvesting: fat graft is harvested from a donor site, usually the thighs or tummy. Harvesting is usually done manually using low-pressure syringe suction to avoid damage to the fat cells.
-
Separation and purification: fat graft is separated from the unwanted elements such as oil, dead cells and blood cells by centrifuge and filtration.
-
Injection: fat graft is injected meticulously to the target site in ultra-tiny droplets using a fine cannula or special injector such as MAFT Gun™.
Post-operative Care**
-
What to expect: Swelling usually peaks on the second to third day after surgery and will gradually subside after that.
-
General care:
-
Avoid direct pressure and hot contact on the target areas
-
Elevate the head during sleep to reduce swelling.
-
Avoid smoking for at least one month. Smoking increases the risk of wound complications and adversely affects the survival of the fat graft.
-
Adequate rest and sleep are helpful for a speedy recovery.
-
Be relaxed and calm. Contact the clinic if there are any queries.
-
-
Medicine: Finish the oral antibiotics as prescribed. Take the painkiller as prescribed when necessary.
-
Wound care: Clean the wound with a clean cotton tip soaked with sterile water/saline. Apply antibiotic ointment. No dressings are required.
-
Physical activity:Avoid heavy physical activity and exercise for at least one month.
-
Follow-up: Come back one week after surgery for suture removal and review.
-
Emergency: If there is heavy bleeding, a rapid increase in swelling or severe pain, immediately contact the clinic/doctor for advice.
** The instructions in this list are only for general guidance. If you have any specific queries or concerns during the post-operative recovery, please contact the clinic for further advice.






