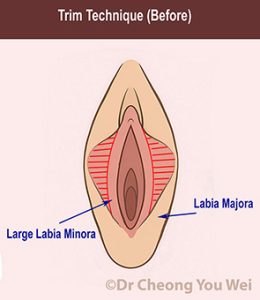
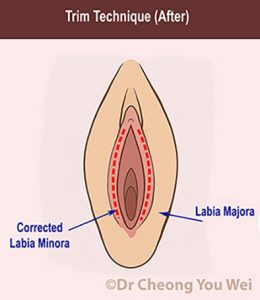
Trim Technique (striped area in red represents the part of labia minora that is removed)
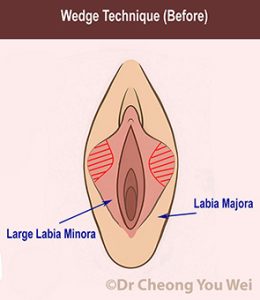
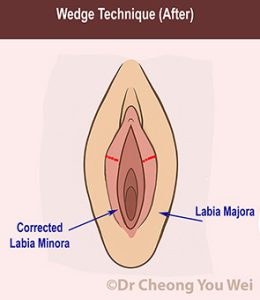
Wedge Technique (striped area in red represents the part of labia minora that is removed)
Labiaplasty is a surgical procedure designed to reduce or reshape the labia minora (inner vaginal lips) for cosmetic, functional, or medical purposes.
Main goals of labiaplasty are:
1. Reduce Labia Minora Size: Shorten the labia minora when they protrude and extend beyond the labia majora.
2. Enhance Aesthetic Appearance: Improve the symmetry, shape, or overall proportion and aesthetic appearance of the vulva.
3. Alleviate Discomfort: Relieve physical discomfort caused by twisting, chafing, or tugging during exercise, sexual activity, or while wearing tight clothing.
4. Improve Hygiene: Reduce excess tissue that may contribute to irritation, recurrent infections, or difficulty maintaining cleanliness.
5. Correct Changes Due to Life Events: Correct changes of the labia caused by childbirth, aging, or hormonal fluctuations.
There are two main surgical approaches to labiaplasty: Trim Technique and Wedge Technique (see Surgery Overview).
Preparation for Surgery
-
Medical Conditions and Allergies: Inform your doctor of any pre-existing medical conditions or drug allergies. All medical conditions must be properly treated and stabilised before surgery
-
Smoking (including vaping): Stop smoking at least one week before surgery. Smoking impairs wound healing and significantly increases the risk of post-operative complications
-
Discontinue the following supplements and medications one week before surgery and continue avoiding them until one week after surgery
-
Avoid all supplements containing vitamin E, ginseng, ginkgo, garlic, fish oil, or any other substances that may increase bleeding. Stop any traditional medicine or herbal remedies with unknown ingredients
-
Stop medications that may increase bleeding—such as aspirin, NSAIDs, and warfarin—should also be stopped. However, please consult your prescribing physician before discontinuing any medication
-
On the day of surgery: wear simple and comfortable clothing. Do not wear any makeup, jewellery and metal objects on your face and body
Surgery Overview
Duration: 1 to 2 hours
Anaesthesia: Local anaesthesia
Hospitalisation: Not required
There are two main surgical techniques:
-
-
-
Trim technique: Excess tissue is trimmed along the edge of the labia, leaving a smooth, straight edge. Trim technique is the simpler technique, enable more precise reduction and it is good for very large or irregularly shaped labia. Trim technique also can address thick or dark edges by removing pigmented tissue along the edge of the labia
-
Wedge technique: A V-shaped “wedge” of tissue is removed from the middle portion of the labia. This technique maintains the natural border and pigmentation along the edge of the labia and preserves a more natural look of the labia.
Post-operative Instructions
What to expect:
1. Swelling is normal and typically peaks around the second to third day post-surgery, gradually improving thereafter.
2. Minor bleeding may occur during the first few days especially during movements. Put a clean sanitary pad over labia for protection.
4. Showering is permitted one day after surgery. Keep the wound clean and dry with soft cotton balls.
General care:
-
-
Avoid smoking. Refrain from smoking for at least one month, as it significantly increases the risk of wound healing complications.
-
Avoid strenuous physical activities, sexual activity, tampon use for 4-6 weeks.
-
Get adequate rest — Ensure you get enough rest and quality sleep to promote a faster and smoother recovery
-
Stay calm and relaxed — Keeping a relaxed and positive mindset helps your body heal. If you have any questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to contact the clinic.
Medicine instructions: Complete the antibiotics — Finish the full course of oral antibiotics as prescribed, even if you feel well. Pain management — Take the prescribed painkillers when necessary, as directed
Wound care instructions:
1. Clean the wound with soft cotton balls soaked with clean water or sterile saline.
2. Apply ointment — After cleaning, apply antibiotic ointment as directed.
Physical activity instructions: Avoid heavy physical activity and strenuous exercise for at least 4-6 weeks to allow proper healing
Follow-up instructions: Return to the clinic one week after surgery for your follow-up appointment and wound assessment.
Emergency instructions: If there is heavy bleeding, a rapid increase in swelling or severe pain, contact the clinic/doctor for advice immediately.
Please Note:
These instructions are meant for general guidance only. If you have any specific questions or concerns during your post-operative recovery, please contact the clinic directly for further advice.
Book a Consultation Appointment Now



