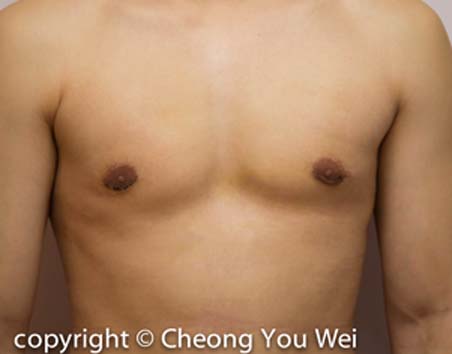
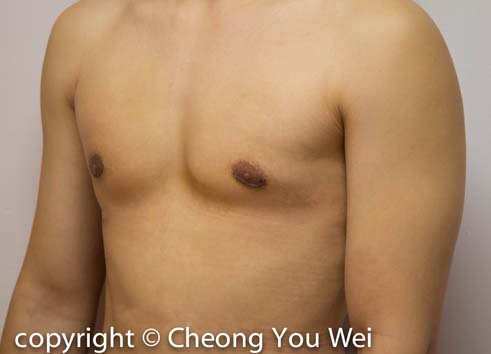
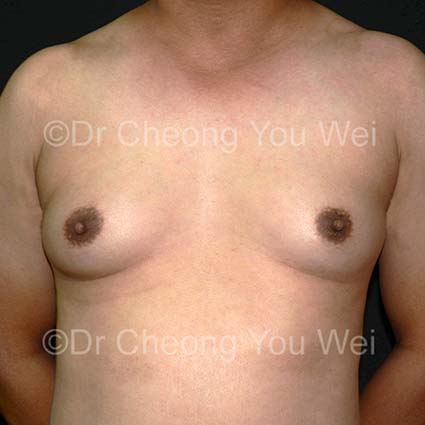
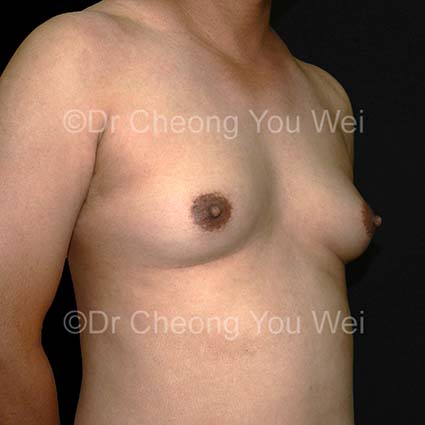
Gynaecomastia (enlarged breasts in Men)
- Before
- After
- Before
- After
- Before
- After
- Before
- After
Gynaecomastia (gynecomastia in US English) refers to the enlargement of breasts in men. It is sometimes referred to as ‘man boobs’. Most of the gynaecomastia can be diagnosed clinically and do no require special diagnostic investigations. Gynaecomastia usually has no serious health implications. However, the enlarged breasts can draw unwanted attention and cause embarrassment to the patient. Gynaecomastia can cause significant psychological and emotional distress to the men with the enlarged breasts.
Causes of gynaecomastia:
-
-
-
Imbalance of testosterone and estrogen hormones in the body. The imbalance can be triggered by conditions that block the effects of testosterone, reduce testosterone level or increase estrogen level in the body. Examples of such conditions include:
-
Natural hormonal changes during puberty. Gynecomastia caused by hormone changes during puberty is fairly common. In most cases, the enlarged breasts will go away after reaching adulthood.
-
Medicine that interfere the activity and metabolism of testosterone and estrogen. Examples are:
-
Anti-androgens used to treat an enlarged prostate, prostate cancer and other conditions. Examples include flutamide, finasteride (Proscar, Propecia).
-
Anabolic steroids and androgens to treat hormone deficiencies, delayed puberty, or to boost muscle mass.
-
Certain antibiotics such as ketoconazole.
-
Certain heart medicine such digoxin.
-
Anti-anxiety medications such as diazepam (Valium) Drugs of abuse are as follows: amphetamines, heroin, methadone, marijuana.
-
-
Health conditions, such as liver problems, malnutrition, hypogonadism, hyperthyroidism, kidney failure
-
Herb and supplements that have excessive estrogenic activity.
-
Aging. Hormonal changes that occur with aging can cause gynecomastia, especially in men who are overweight.
-
-
Increased sensitivity of breast tissues to the normal circulating estrogen level.
-
-
In gynaecomastia, the enlarged breasts consist of two components, glandular tissue, and fatty tissue. Liposuction can remove fatty tissue but not glandular tissue. Glandular tissue would require surgical excision for removal. Thus, the complete removal of gynaecomastia requires the combination of liposuction and surgical excision.
Preparation
-
-
-
Inform the doctor of any pre-existing medical conditions and drug allergy. All medical conditions must be treated and stabilized before surgery.
-
Stop smoking at least one week before surgery. Smoking is harmful to wound healing and increases the risks of other post-operation complications.
-
Stop the following medications and supplements from one week before surgery until one week after surgery.
-
All supplements containing vitamin E, ginseng, ginkgo, garlic, fish oil, and other ingredients that increase bleeding during the procedure. Other supplements, traditional medicine, and herbs, in which ingredients are unknown, have to stop as well.
-
Medicine that increases bleeding during the procedure such as aspirin, NSAIDs, and warfarin. However, you may need to consult your physician who prescribed the medication before you stop them.
-
-
On the day of surgery, wear simple and comfortable clothing. Do not wear any makeup. Do not wear any jewellery and metal objects on the face and body.
-
-
Surgery
Duration: 2-3 hours
Anaesthesia: Local anaesthesia for most cases. General anaesthesia for very large gynaecomastia
Hospitalization: Not required for local anaesthesia cases. General anaesthesia cases are done as daycare cases in the hospital.
Recovery*: Back to work in 3-7 days, light exercise after 1 week, heavy exercise after 4 weeks.
* The actual speed of recovery may vary from person to person.
Surgery Technique: Both liposuction and surgical excision are performed. Liposuction is performed through a small incision (around 3-5mm) on the lower chest and glandular tissue is excised through a semi-circle incision around the lower border of the areola.
Post-operative Care**
-
-
-
What to expect:
-
Swelling usually peaks on the second to third day after surgery and will gradually subside after that.
-
Use a supportive garment to support the chest during the first month.
-
-
General care:
-
Avoid smoking for at least one month. Smoking increases the risk of wound complications.
-
Adequate rest and adequate sleep are helpful for a speedy recovery.
-
Sleep on the back. Avoid sleeping on one side to prevent pressure on the chest.
-
Be relaxed and calm. Contact the clinic if there are any queries.
-
-
Medicine:Finish the oral antibiotics as prescribed. Take the painkiller as prescribed when necessary.
-
Wound care:Clean the wound with a clean cotton tip soaked with sterile water/saline. Apply antibiotic ointment.
-
Physical activity:Avoid heavy physical activity and exercise for at least one month.
-
Follow-up:Come back one week after surgery for the removal of sutures and review.
-
Emergency: If there is heavy bleeding, a rapid increase in swelling or severe pain, immediately contact the clinic/doctor for advice.
-
-
** The instructions in this list are only for general guidance. If you have any specific queries or concerns during the post-operative recovery, please contact the clinic for further advice.