Eyebag Surgery
Eyebag Surgery (Lower Blepharoplasty)
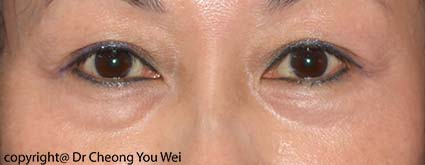
- Before
- After
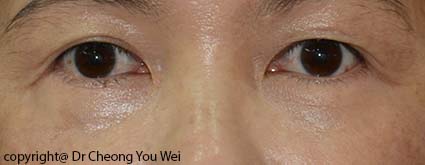
- Before
- After
Eyebag occurs as a normal aging process. However, eyebag may also appear in young people due to hereditary factor, or environmental factors such as lack of sleep and unhealthy lifestyle. Laxity of skin, weakening of supporting structures, and protrusion of fat in the lower eyelid are the primary mechanisms that give rise to eyebag. Eyebag is often associated with dark eye circle and tear trough (a condition where a depression appears at the junction between the lower eyelid and the cheek). The presence of eyebag make a person looks tired and old.
Eyebag surgery, also known as lower blepharoplasty, is minor surgery performed to treat eyebag. There are two types of eyebag surgery: The transconjunctival technique and the transcutaneous technique:
In transconjunctival technique, the incision is made on the conjunctiva on the inner surface of the lower eyelid. There is no external scar. Removal and limited repositioning of orbital fat can be performed. However, removal of excess skin and lifting of mid-face cannot be done with transconjunctival technique. This technique is suitable for those with fat excess only but without skin laxity.
In transcutaneous technique, the incision is made on the skin close to the margin of the lower eyelid. Besides removal and repositioning of the orbital fat, the main advantages of the transcutaneous technique are the ability to remove loose skin, to perform fat grating of the lower eyelid, and to perform lifting of the mid-face. The scar is located very close to the eyelid margin and usually not noticeable after full recovery. This technique is required for patients with laxity and excess skin in the lower eyelid, have a deep tear trough and those who require some mid-face lifting.
The selection of which technique to use depends on the type and severity of the eyebag problem.
Preparation
-
-
-
Inform the doctor of any pre-existing medical conditions and drug allergy. All medical conditions must be treated and stabilized before surgery.
-
Stop smoking at least one week before surgery. Smoking is harmful to wound healing and increases the risks of other post-operation complications.
-
Stop the following medications and supplements from one week before surgery until one week after surgery.
-
All supplements containing vitamin E, ginseng, ginkgo, garlic, fish oil, and other ingredients that increase bleeding during the procedure. Other supplements, traditional medicine, and herbs, in which ingredients are unknown, have to stop as well.
-
Medicine that increases bleeding during the procedure such as aspirin, NSAIDs, and warfarin. However, you may need to consult your physician who prescribed the medication before you stop them.
-
-
On the day of surgery, wear simple and comfortable clothing and do not wear any makeup. Do not wear any jewelry and metal objects on the face and body.
-
Bring a pair of sunglasses on the day of surgery for use after surgery.
-
Don’t wear contact lenses on the day of surgery.
-
-
Surgery
Transconjunctival Technique:
Duration: Half an hour to one hour
Anaesthesia: Local anaesthesia
Hospitalization: Not required.
Recovery*: Back to work in 3-7 days, light exercise after 1-2 weeks, heavy exercise after 3-4 weeks. *The actual speed of recovery may vary from person to person.
Surgery Technique: Transconjunctival Method: The surgeon makes a small opening on the lower eyelid’s inner surface (conjunctival surface). Through the opening, fat is removed and repositioned. There is no resection of skin and no external scar.
Transcutaneous Technique:
Duration: Around 2 hours
Anaesthesia: Local anaesthesia
Hospitalization: Not required.
Recovery*: Back to work in 3-7 days, light exercise after 1-2 weeks, heavy exercise after 3-4 weeks. *The actual speed of recovery may vary from person to person.
Surgery Technique: Transcutaneous Method: an incision is made on the skin close to the margin of the lower eyelid. The surgeon may remove part the extra orbital fat and use the remaining fat to correct the depression at the lower margin of the eyebag. Removal of excess skin is done followed by lifting of the mid-face if it is indicated. The scar is located very close to the eyelid margin and usually not noticeable after full recovery.
Post-operative Care**
-
-
-
What to expect: Swelling usually peaks on the second to third day after surgery and will gradually subside after that. Post-operative pain is usually minimal.
-
General care:
-
Apply cold pack in the first 3 days and then warm pack in the following 3 days. Elevate the head during sleep to reduce swelling.
-
Avoid smoking for at least one month. Smoking increases the risk of wound complications.
-
Use sunglasses for protection when going outdoors.
-
Good rest and adequate sleep are helpful for a speedy recovery.
-
Be relaxed and calm. Contact the clinic if there are any queries.
-
Don’t use contact lenses for at least 2 weeks.
-
-
Medicine: Finish the oral antibiotics as prescribed. Take the painkiller when necessary.
-
Wound care: Clean the wound with a clean cotton tip soaked with sterile water/saline. Apply antibiotic ointment. No dressings are required.
-
Physical activity: Avoid heavy physical activities and exercises for at least one month.
-
Follow-up: Come back one week after surgery for suture removal and review.
-
Emergency: If there is heavy bleeding, a rapid swelling or severe pain, contact the clinic/doctor for advice immediately.
-
-
**The instructions in this list are only for general guidance. If you have any specific queries or concerns during the post-operative recovery, please contact the clinic for further advice.