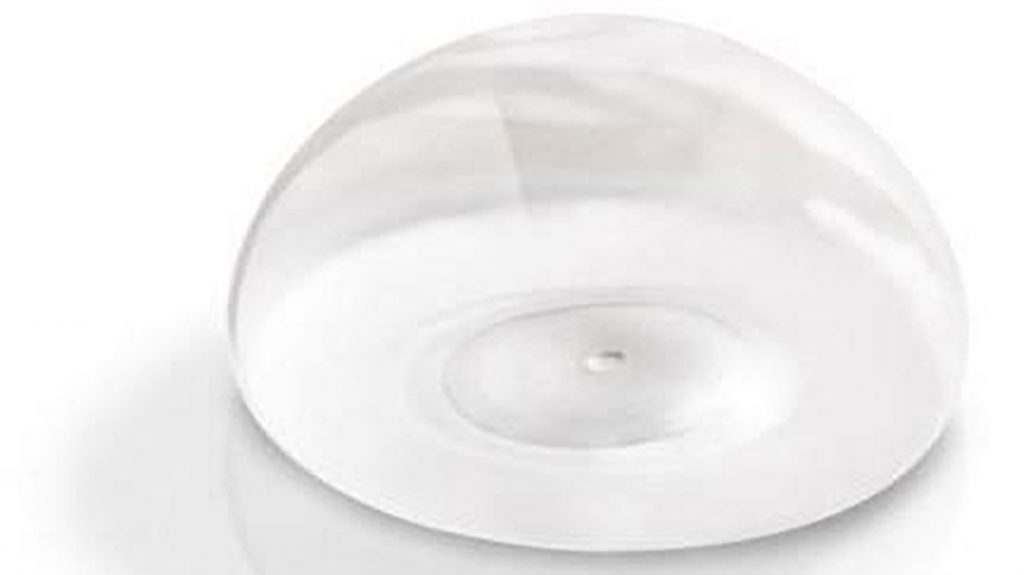
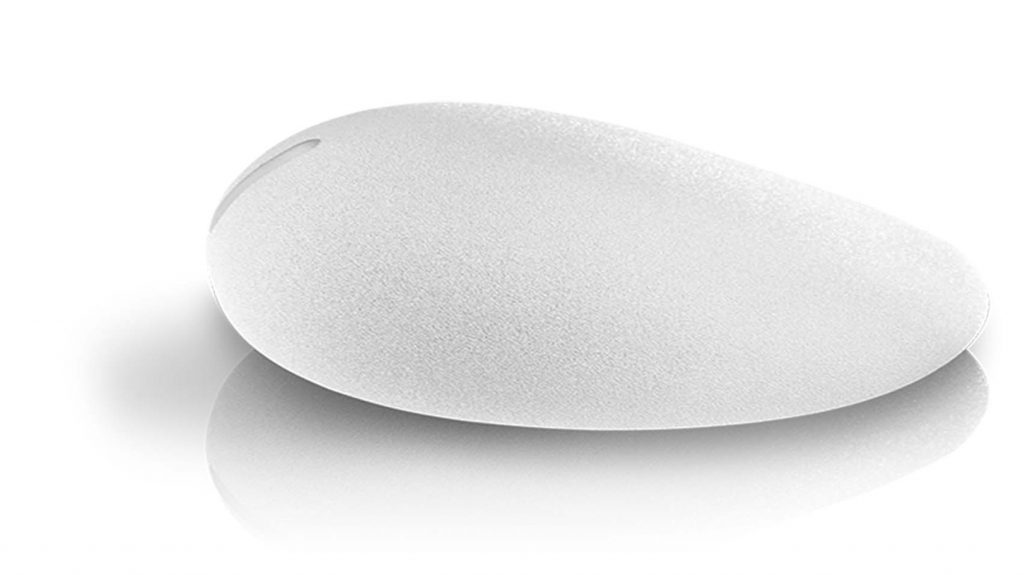
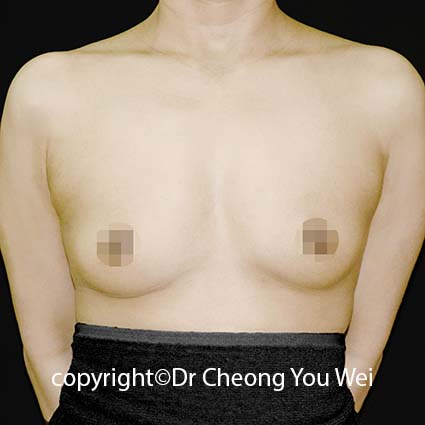
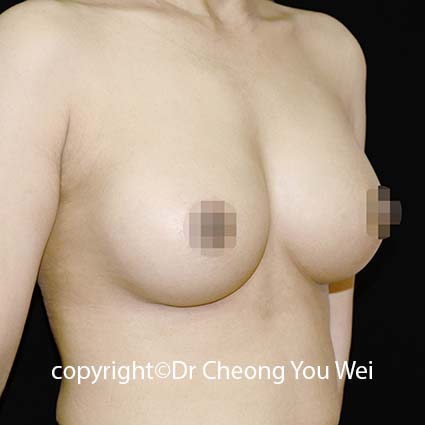
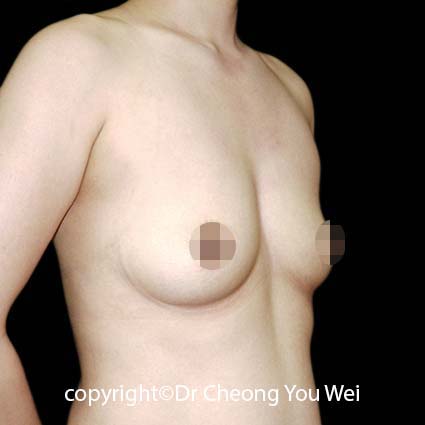
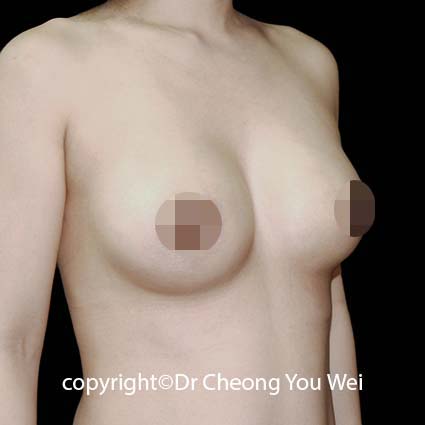
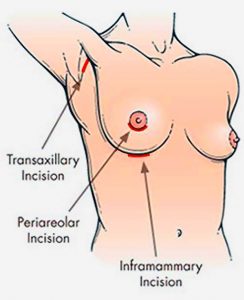
2. Periareolar approach (around the areola): In this method, the incision is placed along the lower half of the areolar border. The scar is usually well-camouflaged by the natural colour and texture of the areola. However, this approach may carry a slightly higher risk of changes in nipple sensation, difficulty with future breastfeeding, and possibility of infection. It may also be unsuitable for patients with small areolae, as the incision may be too short for safe implant insertion.
3. Transaxillary approach (armpit incision):The incision is made within the armpit crease, and a tunnel is created towards the breast to insert the implant. Endoscopic assistance is often used to enhance visibility and accuracy. The main advantage of this approach is the absence of any scar on the breast itself—the scar remains hidden in the armpit. However, because the surgical access is more distant, the technique requires higher technical precision and offers less direct visual control compared to incisions made directly under the breast.
Recovery and Post-operative Care**
Most patients can return to work within 3–7 days, resume light exercise after about 1 week, and return to regular workouts after 4 weeks. Recovery times may vary depending on individual healing and activity levels.
What to Expect After Surgery
1. Swelling is normal and typically peaks around the second to third day post-surgery, gradually improving thereafter.
2. After the procedure, your breasts will be supported with a surgical bra to provide support during healing.
3. Showering is usually permitted 2–3 days after surgery, but you should take care to keep the dressings dry and avoid soaking the surgical area.
4. There may be tight sensation in the chest for one to 2 weeks, especially if large implants are used in patients with tight chest skin.
5. During the early recovery period, the breasts may appear slightly higher and appear fuller in the upper part. This is normal and temporary. Over the next one to two months, they will gradually soften and settle into a more natural, balanced contour.
General care instructions:
1. Wear a supportive bra — Continue wearing the special supportive bra provided by the clinic day and night for at least one month. This helps reduce swelling, supports healing, and maintains the new breast shape.
2. Avoid smoking — Do not smoke for at least one month after surgery. Smoking reduces blood flow and greatly increases the risk of delayed wound healing and other complications.
3. Sleep on your back — Sleep on your back with your upper body slightly elevated, and avoid lying on your sides or stomach to prevent unnecessary pressure on the breasts.
4. Get adequate rest — Allow your body enough time to recover by getting plenty of rest and good-quality sleep. Avoid strenuous activities or heavy lifting until your surgeon advises otherwise.
5. Stay calm and relaxed — A positive and relaxed mindset helps your body heal more effectively. If you have any questions, discomfort, or concerns during your recovery, please contact our clinic — we’re here to support you.
Medicine instructions:
1. Complete the antibiotics — Take the full course of oral antibiotics exactly as prescribed, even if you feel well before finishing them.
2. Pain management — Take the prescribed painkillers when necessary.
Wound Care Instructions:
1. Keep the dressing on — Leave the wound dressing in place until your scheduled review at the clinic.
2. Change if necessary — If the dressing becomes wet, dirty, or loose, replace it with a clean, dry one, or contact the clinic for assistance.
3. After dressing removal — Once the dressing is removed (as advised by your doctor) -Gently clean the wound using a clean cotton tip soaked in sterile water or saline. Apply ointment — After cleaning, apply antibiotic ointment as directed.
Physical Activity Instructions:
1. Limit activity — Avoid lifting heavy objects, stretching your arms excessively, or performing strenuous exercise for at least one month to ensure proper healing.
2. Rest and recovery — Gentle movements are fine, but listen to your body and stop any activity that causes discomfort.
Follow-Up Instructions:
Post-op review —Return for your follow-up appointment one week after surgery for wound inspection and recovery assessment.
Emergency Instructions:
Seek immediate help — If you experience heavy bleeding, a rapid increase in swelling, severe pain, high fever, or notice redness, warmth, or discharge from the wound, please contact the clinic immediately for advice.
Please Note:
These instructions are intended as general guidance. Every patient’s recovery may vary. If you have any doubts, discomfort, or specific concerns, please contact the clinic directly for personalised advice.